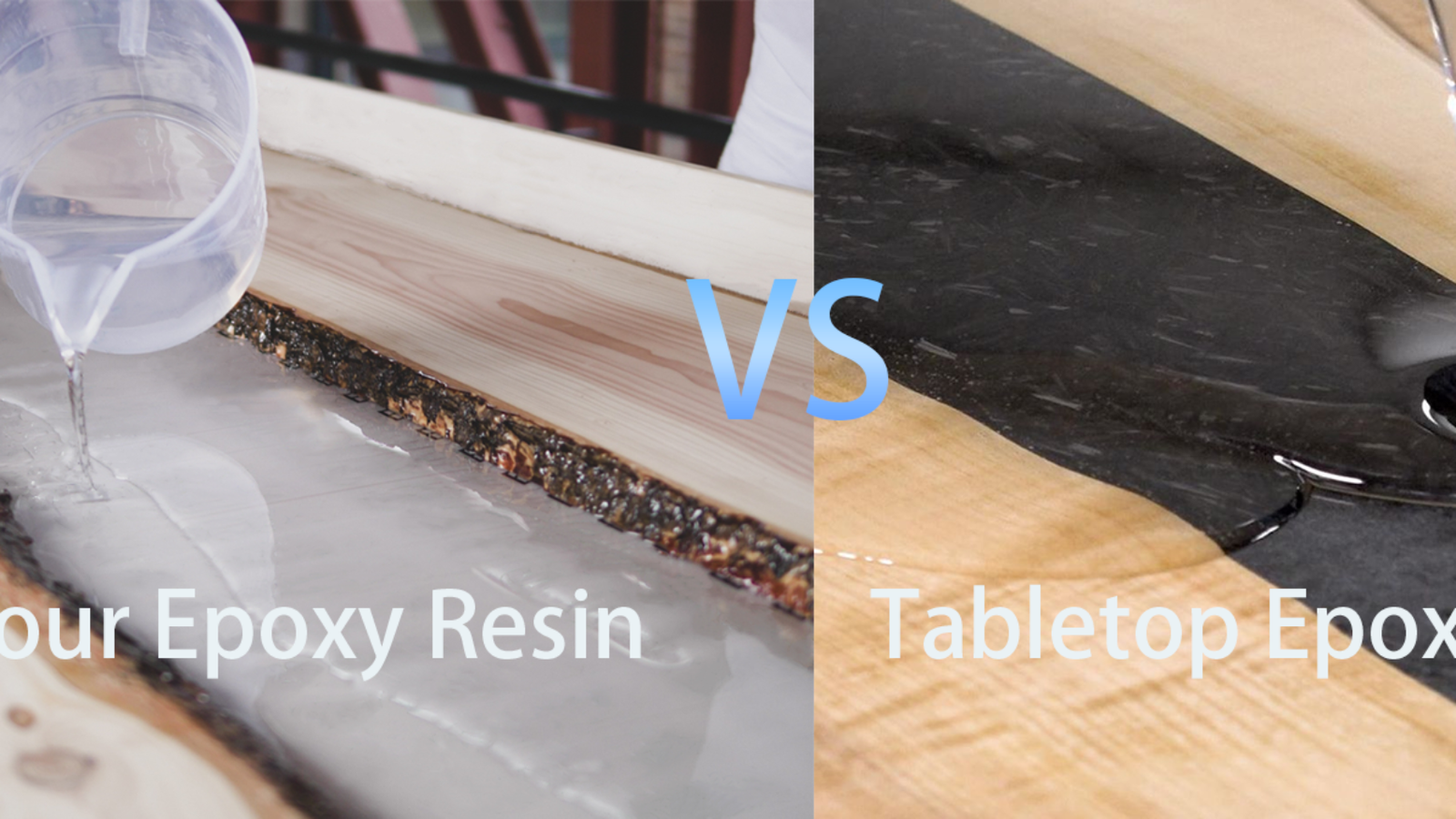
Deep pour epoxy resin (also known as casting epoxy resin) and tabletop epoxy resin (also known as coating epoxy resin) both fall under the two-component epoxy resin system, yet they exhibit significant differences in physical properties, construction requirements, performance characteristics and application scenarios due to distinct core formulation designs and functional orientations. The most crucial difference lies in their working thickness, which in turn leads to a series of consequent differences.
1、Physical Characteristics: Variances in Viscosity and Flowability
Viscosity is the most intuitive difference between the two, directly determining their flow capacity and filling performance.
Tabletop epoxy resin: It has a relatively high viscosity after mixing, with a honey-like consistency and low fluidity. This property allows it to spread slowly and self-level on flat surfaces, ultimately forming a uniform coating of approximately 3 mm in thickness naturally. It can cover surface gaps without additional troweling, making it ideal for creating smooth surface finishes. Some low-quality tabletop epoxy resins only have a self-leveling thickness of about 1.5 mm and require multiple coats to achieve a durable thickness.
Deep pour epoxy resin: It features an extremely low viscosity, almost water-like, with exceptional fluidity. It can easily penetrate wood gaps and mold corners, while facilitating the natural floating and release of air bubbles to avoid bubble residue during thick-layer casting. Its low-viscosity property is the foundation for achieving thick-layer casting, enabling the formation of a relatively thick molded layer in a single application.
2、Construction Parameters: Pouring Thickness, Working Time and Curing Cycle
Tabletop Epoxy Resin: The recommended single pouring thickness is 5–10 mm. If the thickness exceeds this range, the heat generated during curing cannot dissipate in time, which will trigger thermal runaway, leading to surface yellowing, cracking, and shrinkage deformation.It has a relatively short working time, with an operational window of only tens of minutes to 1 hour after mixing. The curing speed is fast: it can achieve initial curing at room temperature in 12–24 hours and complete curing in 24–72 hours. It also supports repainting within a short time (3–6 hours).The mixing ratio is mostly 1:1 by volume, and it has a low operation threshold.
Deep Pour Epoxy Resin: Specifically designed for thick-layer pouring, it can achieve a single pouring thickness of 12–50 mm. To control heat release, its formula adopts a slow-curing system, resulting in an extremely long working time of 3–10 hours or more. For some large-volume pouring products, the working time can be as long as 10 hours, which is sufficient to complete complex mold filling and bubble treatment.Its curing cycle is relatively long: initial curing takes 24–36 hours at room temperature, and complete curing may take several days. It is not suitable for thin pouring; otherwise, it will cause incomplete curing, sticky surfaces, or insufficient hardness.The mixing ratio is mostly 2:1 or 3:1 by volume, with a high requirement for mixing ratio accuracy.
3.Performance Characteristics: Hardness, Heat Resistance, and Stability
Tabletop epoxy resin focuses on surface protection, while deep pour epoxy resin emphasizes molding strength.
Tabletop Epoxy Resin: After curing, it exhibits high hardness, with a Shore D hardness ranging from 70 to 85. It boasts excellent scratch and wear resistance, coupled with superior water and heat resistance, effectively resisting bumps, water stains, and high-temperature contact during daily use. Most products are formulated with UV-protective additives, which reduce yellowing and discoloration caused by sunlight exposure, making them ideal for surfaces exposed to indoor environments for long periods. However, it has poor flexibility and relatively high brittleness, which may lead to cracking under severe impact.
Deep Pour Epoxy Resin: Its hardness after curing is lower than that of tabletop epoxy resin—a deliberate design choice. The deep pour formulation requires a slower reaction rate to enhance toughness and reduce internal stress, resulting in a slightly “softer” yet more flexible material compared to tabletop epoxy resin. It typically has a Shore D hardness of 60 to 75. Its key advantages include low curing shrinkage, excellent dimensional stability after thick-layer molding, and resistance to deformation. Due to its slow curing process, the internal stress is evenly distributed, ensuring overall toughness that surpasses that of tabletop epoxy resin. It also offers good yellowing resistance, but its UV protection capability is generally weaker than that of tabletop epoxy resin, so it may still discolor when exposed to prolonged sunlight.
4、Applicable Scenarios: Functionality Determines Application Scope
The applicable scenarios of the two are strictly aligned with their performance characteristics and cannot be arbitrarily substituted, otherwise it will lead to project failure.
Tabletop Epoxy Resin: Its core application is surface coating protection, suitable for creating flat, high-gloss, and durable surface layers. Typical applications include sealing the surfaces of dining tables, bar counters, countertops, and solid wood furniture, as well as curing the surface layers of coasters, decorative panels, and mixed-media artworks. It can be mixed with pigments such as mica powder and alcohol ink to create colorful decorative surfaces, while also sealing wood and preventing deformation caused by moisture absorption. Note that if it is used outdoors, additional UV protection additives must be added or UV-protective tabletop epoxy resin should be purchased.
Deep Pour Epoxy Resin: Its core application is three-dimensional molding and thick-layer filling, suitable for the production of molded parts that require a certain thickness. Typical applications include river tables (filling wood gaps), resin castings, silicone mold molding (jewelry, pen holders, ornaments), large-scale artworks encapsulation, and building gap filling. Objects such as metal, wood, and flowers can be embedded and encapsulated within it to create a transparent and three-dimensional effect. Due to its insufficient hardness, large molded parts (such as river table tops) usually require an additional layer of tabletop epoxy resin to be applied on the surface, balancing thickness and surface durability.
5.Summary and Selection Principles
Essentially, tabletop epoxy resin is a “coating resin” focused on thin-layer protection and high-gloss decoration; deep pour epoxy resin is a “molding resin” designed for thick-layer filling and three-dimensional molding. The selection of the two must follow the “thickness matching” principle:
For thin-layer (1–3 mm) surface protection and high-gloss decoration, with a focus on fast curing and high hardness, choose tabletop epoxy resin.
For thick-layer (≥3 mm) molding, gap filling, and object encapsulation, requiring bubble and shrinkage control, choose deep pour epoxy resin.
For complex projects (e.g., river tables), a combination can be used: deep pour epoxy resin fills gaps to achieve the required thickness, while tabletop epoxy resin is applied to the surface to enhance hardness and wear resistance.